![]() body | color | collections | commodity | cube | document | fabric | fetish | gender | glass | home | identity | living | machine | metal | minimal | mobility | narrative | olfactory | organic |
body | color | collections | commodity | cube | document | fabric | fetish | gender | glass | home | identity | living | machine | metal | minimal | mobility | narrative | olfactory | organic |
![]() pain | paper | plastic | plugs | power | protective | rectangular | ritual | round | sound | souvenir | spiritual | style | text-based | time | tool | touch | uniform | value | visual | warm | wood
pain | paper | plastic | plugs | power | protective | rectangular | ritual | round | sound | souvenir | spiritual | style | text-based | time | tool | touch | uniform | value | visual | warm | wood
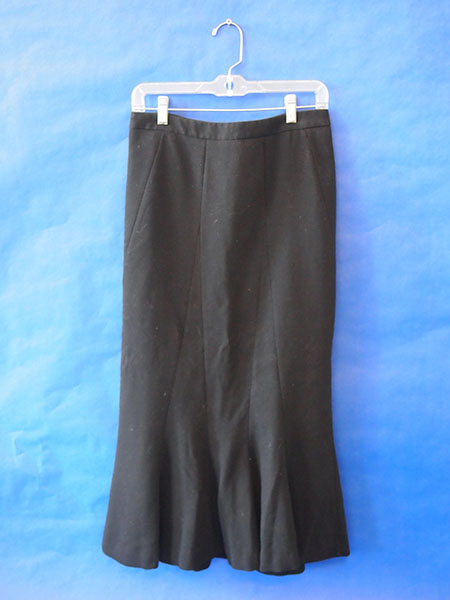
| Clothing: Black Long Skirt with Zipper on Back | |||
Narrative: H&M; Black long skirt with zipper on back; Size 6; Made in China; Shell – 63% polyester, 34% rayon, 3% spandex Lining – 100% polyester. In 1946 American du Pont de Nemours and Co. purchased right to manufacture polyester in the United States nearly reversing fiber rations in the U.S. in the 1950’s. Derived from coal, air, water, and petroleum. Principle ingredient in manufacturing is ethylene (from petroleum). Fibers are formed from a chemical reaction between acid and alcohol. The structure of the molecule created repeats throughout the fiber length. Basic forms of manufacturing are filament, staple, tow, and fiberfill. Does not absorb moisture but does absorb oil; perfect for application of water, soil, fire resistant finishes. Does not stretch once pre-shrunk, does not get damaged by mildew. Spandex fibers are produced in four different ways: melt extrusion, reaction spinning, solution dry spinning, and solution wet spinning. All of these methods include the initial step of reacting monomers to produce a prepolymer. Once the prepolymer is formed, it is reacted further in various ways and drawn out to make the fibers. The solution dry spinning method is used to produce over 94.5% of the world's spandex fibers. The first step is to produce the prepolymer. This is done by mixing a macroglycol with a diisocyanate monomer. The two compounds are mixed in a reaction vessel to produce a prepolymer. A typical ratio of glycol to diisocyanate is 1:2. The prepolymer is further reacted with an equal amount of diamine. This reaction is known as chain extension reaction. The resulting solution is diluted with a solvent to produce the spinning solution. The solvent helps make the solution thinner and more easily handled, and then it can be pumped into the fiber production cell. H&M's supply chain consists of Factory Employees, Second-tier Suppliers, Suppliers, Shippers, Auditors, Merchandisers, and Buyers. Cotton is farmed and picked in India, China, and Turkey Clothing design and samples made in Stockholm, Sweden where the headquarters are located. Dying mills and water supply near the Yangtze River in China. Washed and cleaned with water from the Brahmaputra River in Assam. Made and manufactured in Dhaka, Bangladesh; Bangkok, Thailand; Bangalore, Karnataka, India; Bandung, Indonesia; among others. H&M clothing labels and tags are printed in Stockholm, Sweden (approved by the EU Ecolabel Company). Papers are made from Forest Stewardship Council trees (FSC certified). Final products are sent to Hamburg, Germany where they are distributed to store locations. In a recent study commissioned by Greenpeace International, several major clothing brands including H&M were found guilty of using nonylphenol ethoxylates (NPEs) in the manufacturing process. This chemical breaks down into toxic nonylphenol (NP), which has hormone-disrupting properties that persist over time and can be hazardous even at low levels. |
 |
||
![]()