![]() body | color | collections | commodity | cube | document | fabric | fetish | gender | glass | home | identity | living | machine | metal | minimal | mobility | narrative | olfactory | organic |
body | color | collections | commodity | cube | document | fabric | fetish | gender | glass | home | identity | living | machine | metal | minimal | mobility | narrative | olfactory | organic |
![]() pain | paper | plastic | plugs | power | protective | rectangular | ritual | round | sound | souvenir | spiritual | style | text-based | time | tool | touch | uniform | value | visual | warm | wood
pain | paper | plastic | plugs | power | protective | rectangular | ritual | round | sound | souvenir | spiritual | style | text-based | time | tool | touch | uniform | value | visual | warm | wood
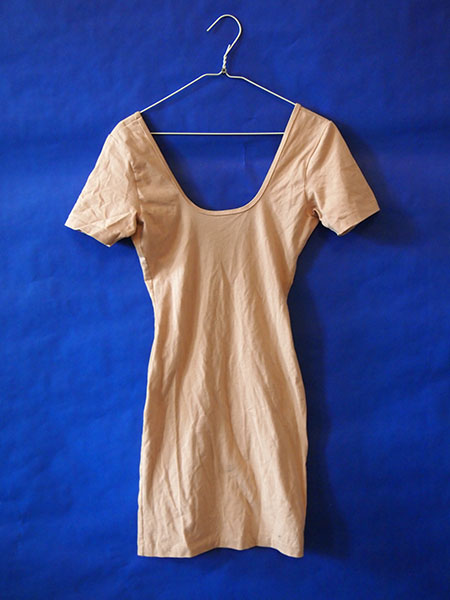
| Clothing: Beige Off-the-Shoulder Dress | |||
Narrative: American Apparel I purchased this at American Apparel in Williamsburg, Brooklyn before a fundraiser party for the Waterpod in 2009. Spandex fibers are produced in four different ways: melt extrusion, reaction spinning, solution dry spinning, and solution wet spinning. All of these methods include the initial step of reacting monomers to produce a prepolymer. Once the prepolymer is formed, it is reacted further in various ways and drawn out to make the fibers. The solution dry spinning method is used to produce over 94.5% of the world's spandex fibers. The first step is to produce the prepolymer. This is done by mixing a macroglycol with a diisocyanate monomer. The two compounds are mixed in a reaction vessel to produce a prepolymer. A typical ratio of glycol to diisocyanate is 1:2. The prepolymer is further reacted with an equal amount of diamine. This reaction is known as chain extension reaction. The resulting solution is diluted with a solvent to produce the spinning solution. The solvent helps make the solution thinner and more easily handled, and then it can be pumped into the fiber production cell. The spinning solution is pumped into a cylindrical spinning cell where it is cured and converted into fibers. Power generation and supply; Cotton farming; Truck transportation; Oil and gas extraction; Other basic organic chemical manufacturing; Artificial and synthetic fibers and filaments manufacturing; Hosiery and sock mills; Petroleum refineries; Iron and steel mills; Plastics material and resin manufacturing. Water withdraw includes: Cotton farming; Grain farming; Artificial and synthetic fibers and filaments manufacturing; Hosiery and sock mills; Power generation and supply; Fiber, yarn, and thread mills; Other basic organic chemical manufacturing; Paperboard mills; Paint and coating manufacturing; Synthetic dye and pigment manufacturing. |
 |
||
![]()